Windows Virtualization: Revolutionizing PC Computing
Windows Virtualization refers to Microsoft’s suite of technologies that enable the creation and management of virtual environments on a physical PC or server. It allows multiple operating systems or isolated applications to run concurrently, optimizing the use of hardware resources and providing enhanced flexibility, security, and scalability. Virtualization is increasingly critical for businesses, developers, and IT professionals who need to manage multiple systems efficiently, test software, or host remote environments.
The main technologies under the Windows Virtualization umbrella include Hyper-V, Windows Virtual Desktop (now Azure Virtual Desktop), Windows Sandbox, and Windows Containers. Each offers unique benefits for different use cases, making Windows Virtualization a versatile solution for both personal and enterprise needs.
Windows Virtualization brings powerful tools for PC users, whether it’s creating isolated environments for testing, running cloud-based virtual desktops, or managing multiple virtual machines with Hyper-V. By integrating features like PC-Concept, which simplifies and automates the control and management of virtual environments, Microsoft continues to enhance the flexibility and capabilities of PCs for personal and business use.
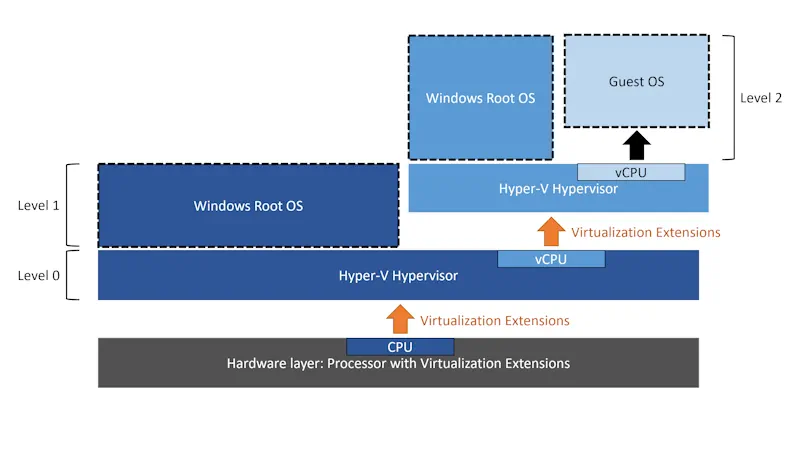
Hyper-V: The Core of Windows Virtualization
Hyper-V is Microsoft’s hypervisor technology that allows the creation of virtual machines (VMs) on a physical PC or server. It is available in Windows Server and Windows 10/11 Pro and Enterprise editions. Hyper-V enables users to run multiple operating systems on the same hardware, improving resource efficiency.
Key Features of Hyper-V:
- Multiple OS Support: Hyper-V allows Windows and Linux operating systems to run as VMs on the same machine.
- Resource Management: Users can allocate CPU, memory, and network resources individually for each VM, making it ideal for testing environments or server consolidation.
- Isolation: Virtual machines are isolated from each other, ensuring that applications or processes running in one VM do not affect others.
This makes Hyper-V an excellent choice for businesses that need to host multiple servers or developers who require isolated environments for testing.
Windows Virtual Desktop: The Cloud-Based Virtualization for PCs
Formerly known as Windows Virtual Desktop, Azure Virtual Desktop (AVD) enables businesses to run a fully virtualized Windows environment from the cloud. AVD delivers Windows 10 or 11 desktops to users on any device, leveraging the power of Azure for scalability, security, and remote access.
Key Features of Azure Virtual Desktop:
- Remote Desktop Experience: Users can access a full Windows desktop experience remotely from their PCs, tablets, or smartphones.
- Cost Efficiency: AVD allows businesses to reduce the overhead costs associated with maintaining physical infrastructure.
- Security: It integrates with Azure’s security features, ensuring data and applications are protected in the cloud.
This service is particularly useful for businesses that have embraced remote work or need to provide employees with a consistent desktop experience regardless of location.
Windows Sandbox: A Lightweight Virtual Environment for PC Users
Windows Sandbox is a lightweight, temporary virtualized environment that comes built into Windows 10/11 Pro and Enterprise editions. It’s designed for users who need to run untrusted software or files without risking their main PC environment.
Key Features of Windows Sandbox:
- Disposable Environment: Once the session is closed, all data, applications, and settings within the sandbox are deleted.
- Security: It runs in isolation from the main operating system, ensuring that any malicious code does not affect the host PC.
- No Setup Required: Unlike traditional virtual machines, Windows Sandbox requires no configuration, making it an easy solution for quick, safe testing.
This feature is ideal for professionals who frequently download or test untrusted files on their PCs, offering an added layer of protection.
Windows Containers: Virtualization for Applications on PCs
Windows Containers allow for the virtualization of applications, enabling them to run in isolated environments without the need for a full virtual machine. This technology shares the host OS kernel but keeps the applications isolated from each other and the rest of the system.
Key Features of Windows Containers:
- Lightweight: Containers are faster to start and use fewer resources than traditional VMs.
- Scalability: Multiple containers can run on the same physical PC or server, making it ideal for cloud-native applications.
- Docker Support: Windows Containers are compatible with Docker, a leading platform for managing containerized applications.
Windows Containers are a popular choice in development environments where microservices and cloud-native applications are prevalent.
Benefits of Windows Virtualization for PCs
Virtualization offers several key benefits for PC users:
- Resource Optimization: By running multiple operating systems or applications on the same physical PC, users can make more efficient use of their hardware resources.
- Enhanced Security: Virtual environments provide isolation, preventing malware or system crashes in one environment from affecting the entire PC.
- Flexibility: Users can test different configurations, software, or operating systems without needing multiple physical devices.
